Bradford VTS Online Resources:
OSCE
Prescribing
DOWNLOADS
path: OSCE database
WEBLINKS
- x
Videos

The universal GP Training website for everyone, not just Bradford. Created in 2002 by Dr Ramesh Mehay
path: OSCE database

Bradford VTS Clinical Resources
path: PRESCRIBING/prescribing-analysis-tools
……………………………………..
Information provided on this medical website is intended for educational purposes only and may contain errors or inaccuracies. We do not assume responsibility for any actions taken based on the information presented here. Users are strongly advised to consult reliable medical sources and healthcare professionals for accurate and personalised guidance – especially with protocols, guidelines and doses.
COME AND WORK WITH ME… If you’d like to contribute or enhance this resource, simply send an email to rameshmehay@googlemail.co.uk. We welcome collaboration to improve GP training on the UK’s leading website, Bradford VTS. If you’re interested in a more active role with www.bradfordvts.co.uk (and get your name published), please feel free to reach out. We love hearing from people who want to give.
……………………………………..
Elementor team. Play with this widget and see how slow it is on every page. Try to
This site is for doctors and many doctors around the world rely on it. It provides free medical information and so it is important that this site runs smoothly. But some of my very small team wont now use it to update the website because they say it is so incredibly slow. Please help so we can continue supporting doctors around the world.
Many thanks
Dr Ramesh Mehay
SYMPTOMATIC
Symptoms of hyperglycaemia (polyuria /polydipsia, unexplained weight loss. visual blurring, genital thrush, lethargy) plus either:
HbA1c: 48mmol/mol or higher (LAB TESTING) (Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed in adults who are not pregnant and do not have haemoglobinopathy or haemolytic anaemia by a glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 48 mmol/mol or above.
The WHO state that diagnosis should be confirmed with a repeat HbA1c test, unless clinical symptoms and plasma glucose levels >11.1mmol/l are present in which case further testing is not required.)
FBG: >7.0mmol/L or higher x2
Dip urine to check for ketones
ASYMPTOMATIC
In the absence of symptoms – 2 abnormal results on separate days are required for the diagnosis.
Results:
May not be accurate in the following cases:
Patients with haemoglobinopathy – the labs test for this and will detect abnormalities.
A diagnosis of diabetes has important legal and medical implications for the patient and it is therefore essential to be secure in the diagnosis.
A diagnosis should never be made on the basis of glycosuria.
A stick reading of finger prick should be confirmed by a venous sample, as per NICE guidelines.

What is it?
When we mention the cytochrome P450 system, most doctors just want to turn around and run away! So, let’s demystify it once and for all. The cytochome P450 (CYP45) system is basically the liver’s enzyme system. The CYP450 is so called because it is found within the membranes of a cell (hence CYTO). It contains a haem pigment (hence CHROME and P). And it absorbs light at a wavelength of 450nm. It has quite a number if functions…
LIFESTYLE
BMI
Aim for healthy BMI <25 – consider dietition, Orlistat, other dietary measures & EXERCISE
ALCOHOL
Not to exceed recommended limits. (14 units men and women)
SMOKING
Stop!
BLOOD PRESSURE
Active management is essential!
Over half of all diabetics are hypertensive. Trials have shown that excellent BP control reduces retinopathy, nephropathy, strokes, heart failure and MI. BP control is as important as glycaemic control! TARGET < 130/80
Treatment
LIPIDS AND CVD RISK (see lipid modification protocol)
Offer generic Atorvastatin 40mg (Bradford Healthy Hearts) if their Q risk >10% (aged between 18-84 yrs), have been diabetic for > 10 years or, over 40 years old. Target chol <4mmol/l
For diabetics with established CVD offer secondary prevention or Chol > 4mmol/l – Atorvastatin 80mg
Triglycerides:
If TG level remains high (above 4.5mmol/l) please ref to CKS guidance on lipid modification or in-house lipid modification protocol.
Do not routinely offer Nicotinic acid or Omega fish oils.
MICROALBUMINURIA AND CKD
ANTIPLATELETS
Why is the cytochrome P450 important?
Because so many drugs (including nutrients and herbal therapies) are metabolised via the CYP450 system. This system can be inhibited or induced by drugs. And that then leads to drug-drug interactions and all sorts of adverse reactions. Drugs that cause CYP450 drug interactions are referred to as either inhibitors or inducers.
And what makes it worse, is that there is genetic variability in about 7% of people. For example, many clinicians believe that post menopausal women recieving tamoxifen for early breast cancer should be tested for their type of CYP2D6 genotype as it may be valuable in selecting the type of adjuvant homonal therapy to offer. And of course CYP2D6 inhibitors should be avoided in tamoxifen-treated women.
And patients come to us with often co-morbidity. It would be nice if the world was just full of people with just the one thing. But it isn’t. It’s a lot more complex. It’s not uncommon for a patient withy hypertension and bad lipids to present to us at some point with depression, for instance. Did you know that several antidepressants are CYP450 inhibitors (i.e. reduce metabolism of other drugs). The effect on drugs like halperidol or metoprolol will then be accentuated.
In the case of grapefruit juice, there are numerous medications known to interact with grapefruit juice including statins, antiarrhythmic agents, immunosuppressive agents, and calcium channel blockers. Furthermore, the inhibition of the enzyme system seems to be dose dependent; thus, the more a patient drinks, the more the inhibition that occurs. Additionally, the effects can last for several days if grapefruit juice is consumed on a regular basis. Luckily, the effect of this is not seen with other citrus juices.
Examples of INDUCERS
(i.e. speeds up metabolism of other drug, so it may not be as effective)
Mnemonic: SCRAP GPS
Examples of INHIBITORS
(i.e. slows down the metabolism of other drug, so it’s effects may be accentuated)
Mnemonic SICKFACES.COM G
Examples of drugs which interact with cP450 inducers/inhibitors
Medication | Mode of action | Side effects | Cautions (check BNF for more detail) | Dose |
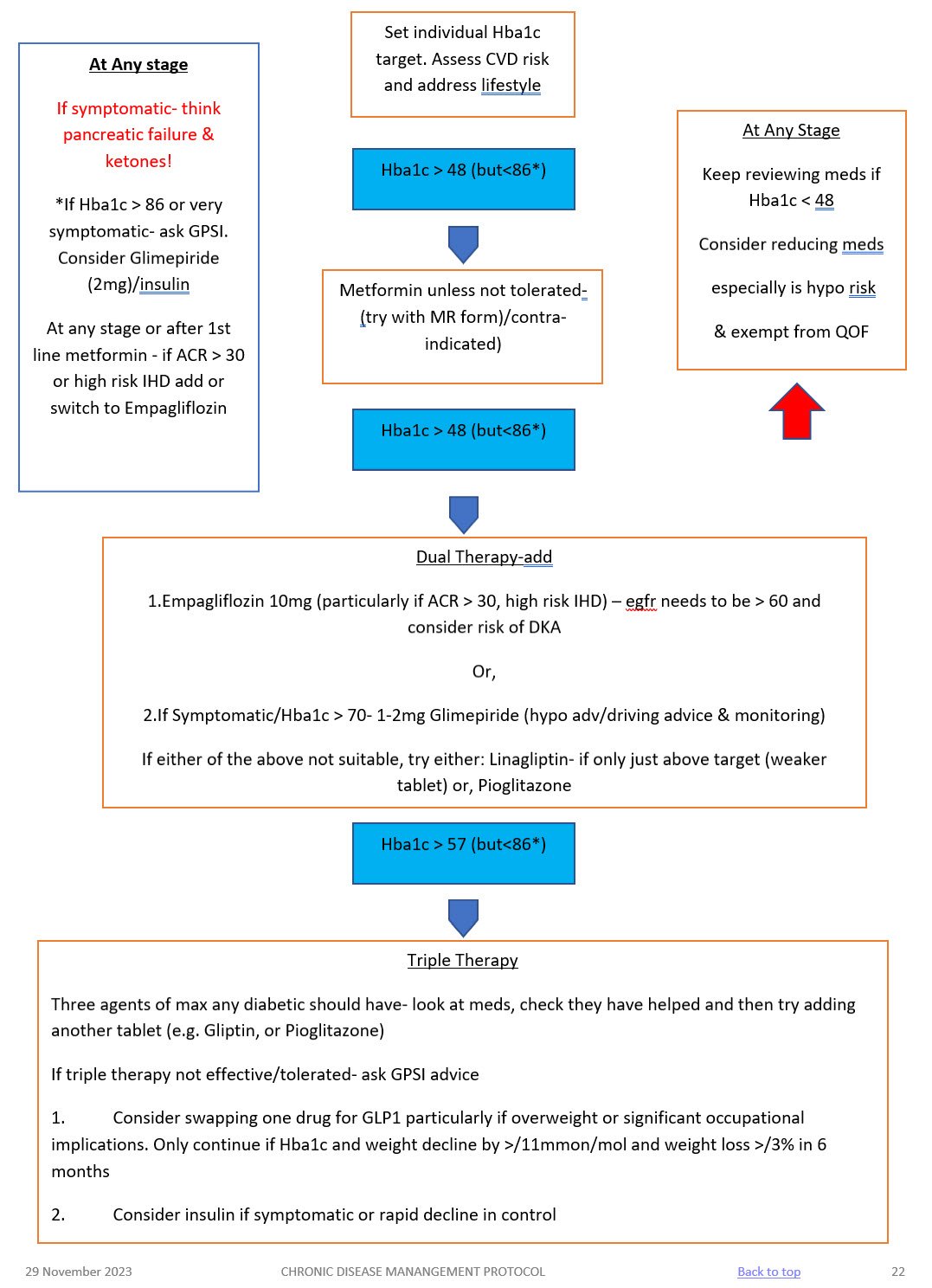
METFORMIN 1st line treatment, unless BMI <25 (23 in South Asian population) Low Hypo risk Reduces CVD risk, weight neutral | Helps to stop the liver producing new glucose. It helps to overcome insulin resistance by making insulin carry glucose into muscle cells more effectively.
| Main side effect if GI affects, generally dose dependent-can be reduced with gradual increase in dose over several weeks or trying modified release Metformin Also: metallic taste, reduced absorption of vitamin B12, build up of lactic acid in the blood, allergic reaction and liver problems. | STOP/DO NOT USE IF eGFR <30 ml/min *Lactic acidosis- care if eGFR < 45ml/min. Document that advice has been given to stop these tablets if they become dehydrated (restart when eating normally again) *GI side effects. Titrate dose slowly to reduce side effects NOTE IF ALT> 3 TIMES NORMAL | Start at 500mg ideally with evening meal, increasing to 1g with evening meal after a week if they have no side effects. Max dose 2 gram over 4 weeks. Consider slow release for to reduce tablet load or if they are struggling with GI side effects.
|
SGLT-inhibitor Empagliflozin Low hypo risk Can help with weight loss | Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor that prevents glucose reuptake in the kidney, leading to the excretion of excess glucose in the urine. | Polyuria, polydipsia, thrush. UTI, fluid depletion Increased risk of amputation- avoid if h/o leg ulcers | Only start if Cr Clearance > 60. Care if > 75 years. Risk of postural hypotension. Care needed if they have skin ulcers – risk of amputation. Document advice about normoglycaemic ketoacidosis and give ketostix. | Empagliflozin 10mg. Can be increased to 25mg. Expensive so only continue if there is a clear response after 6 months |
SULPHONYLUREA (SU) Glimepiride Risk of hypos Good if rapid response is needed. | They work by stimulating cells in the pancreas to make more insulin. They also help insulin to work more effectively in the body.
| Weight gain. Hypoglycaemia, gastrointestinal side effects, low sodium, facial flushing and intolerance of alcohol, allergies etc.
| Can cause hypoglycaemia, particularly if there is renal impairment or they are elderly. Consider occupation – hypos if not eating regularly, fasting. Make sure you give and document advice about hypos. Make sure they are able to test their blood glucose – issue glucometer, test strips, lancets and sharps bin. (SGBM) Document advice about driving/insurance. | Start at 1mg and titrate up to 4mg depending on glucose level. Should have an effect on Hba1c over a 2 month period. |
GLIPTIN Do not cause weight gain and encourages patient satiety. Although they probably reduce Hba1c levels less than other drug treatments. Low hypo risk | They work by blocking the action of the enzyme, DPP-4, which destroys the hormone Incretin.
| Gastro-intestinal effects, oedema, headache, Avoid if h/o Pancreatitis or heart failure or liver problems. | *Expensive- only continue if they meet NICE guidance. *Not v powerful max likely reduction ~ 11 mmol/mol *Do not use if a h/o pancreatitis *Monitor egfr at reviews *Don’t use if heart failure risk | Linagliptin 5mg if eGFR < 50 |
GLITAZONE Pioglitazone Low hypo risk Consider in people with very significant features of metabolic syndrome. South Asian | Reducing insulin resistance. Improving insulin sensitivity.
| Oedema esp if heart failure or at risk. Rare reports of liver dysfunction. Weight gain, gastro-intestinal side effects, headache, dizziness.
| Discuss with member of Level 2 team before starting. Avoid if they have heart failure or risk of fluid overload Avoid if h/o bladder cancer, undiagnosed haematuria Avoid if fracture risk Monitor LFTs at each diabetic review. Annual urine dip looking for haematuria | Pioglitazone:15mg-30mg. A six month period may be needed to really see an effect from these tablets. NICE recommends that they are only continued if at least a 11 mmol/l reduction in Hba1c is seen within 6 months of starting the treatment.
|
GLP-1 mimetic/insulin | Discuss with Level 2 doctor |
|
Advise patients the following: if you do go down with a cold, flu or any other illness…
Advise patients of the following:
www.ehic.org.uk, / 0845 605 0707
Consider availability of insulin if travelling abroad for long periods.
Interpreting blood results on pathology template – Remember frailty
Any concerns – send message to Level 2 team
Using the SystmOne Template (CDM) for Diabetes.
See CDM review table
TARGETS AT A GLANCE
Diabetes in pregnancy is associated with risks to the woman and the developing fetus.
Planning a pregnancy
Women planning a pregnancy should be referred to a diabetes pre-conception clinic.
Pre-pregnancy planning includes:
Review of medications
Gestational diabetes
All patients require an ANNUAL HbA1c in view of their elevated risk of Type 2 diabetes. Please add an ‘AT RISK OF DIABETES’ recall to their notes.
What is it?
When we mention the cytochrome P450 system, most doctors just want to turn around and run away! So, let’s demystify it once and for all. The cytochome P450 (CYP45) system is basically the liver’s enzyme system. The CYP450 is so called because it is found within the membranes of a cell (hence CYTO). It contains a haem pigment (hence CHROME and P). And it absorbs light at a wavelength of 450nm. It has quite a number if functions…
Why is the cytochrome P450 important?
Because so many drugs (including nutrients and herbal therapies) are metabolised via the CYP450 system. This system can be inhibited or induced by drugs. And that then leads to drug-drug interactions and all sorts of adverse reactions. Drugs that cause CYP450 drug interactions are referred to as either inhibitors or inducers.
And what makes it worse, is that there is genetic variability in about 7% of people. For example, many clinicians believe that post menopausal women recieving tamoxifen for early breast cancer should be tested for their type of CYP2D6 genotype as it may be valuable in selecting the type of adjuvant homonal therapy to offer. And of course CYP2D6 inhibitors should be avoided in tamoxifen-treated women.
And patients come to us with often co-morbidity. It would be nice if the world was just full of people with just the one thing. But it isn’t. It’s a lot more complex. It’s not uncommon for a patient withy hypertension and bad lipids to present to us at some point with depression, for instance. Did you know that several antidepressants are CYP450 inhibitors (i.e. reduce metabolism of other drugs). The effect on drugs like halperidol or metoprolol will then be accentuated.
In the case of grapefruit juice, there are numerous medications known to interact with grapefruit juice including statins, antiarrhythmic agents, immunosuppressive agents, and calcium channel blockers. Furthermore, the inhibition of the enzyme system seems to be dose dependent; thus, the more a patient drinks, the more the inhibition that occurs. Additionally, the effects can last for several days if grapefruit juice is consumed on a regular basis. Luckily, the effect of this is not seen with other citrus juices.
Examples of INDUCERS
(i.e. speeds up metabolism of other drug, so it may not be as effective)
Mnemonic: SCRAP GPS
Examples of INHIBITORS
(i.e. slows down the metabolism of other drug, so it’s effects may be accentuated)
Mnemonic SICKFACES.COM G
Examples of drugs which interact with cP450 inducers/inhibitors
Whst is the QT interval?
The QT interval is the measure of time between the onset of the Q wave and the end of the T wave. This interval represents the time that depolarization and repolarization of the ventricle occur.
Why is this important?
To understand why this is important, we need to talk for just a moment about the refractory period. After the cardiac cells depolarize, they must “recharge” or repolarize. This “recharging” phase is what we refer to as the refractory period. Generally speaking, a refractory period is one in which the cell is unable to have another action potential. More specifically, there’s an “absolute refractory period” where no new action potentials can take place…which is followed by a “relative refractory period” where an action potential COULD occur, if the stars are aligned, Venus is in Scorpio and everything falls into perfect place. But here’s the thing…you don’t want an action potential to occur during this time. If an electrical stimulus hits during this relative refractory period, premature depolarization can occur before the cardiac cells are completely repolarized…the result is that the heart can go into dangerous and deadly ventricular arrhythmias and ain’t nobody got time for that!
And this, ladies and gentlemen, is why we keep such a close eye on the QT interval.

Below is Torsades de Pointes

Definitions
Definitions for QT prolongation vary in the literature, but commonly the following are used
When should I worry?
Below is Torsades de Pointes

So… look at the ECG!
Correct the QT interval using the fomula at MDCALC
Determine the increase from baseline
Please note, this is NOT a comprehensive list. This is a list of common drugs seen in Primary Care/General Practice. You can see from the list below that a lot of drugs used in psychiatry do this.
MODERATE EFFECT
By moderate effect we mean an 10-20 msec increase in QT prolongation, which is significant. If the delay is greater than 20 msec, the risk is significant and serious!
Antibiotics | Erythromycin | Clarithromycin | Azithromycin | Ciprofloxacin |
Antidepressants | Citalopram | Escitalopram | Clomipramine | Quetiapine |
Anti-emetics | Ondansetron |
|
| |
Antifungals
| Fluconazole |
|
|
|
Anti-pychotics | Haloperidol | Chlorpromazine | Risperidone | Amisulpiride, |
Addiction Rx | Methadone (esp dose > 100mg) | Lofexidine |
|
|
Cardiac drugs | Amiodarone | Sotalol | Flecainide |
|
Miscellaneous | Hydroxyzine (anti-itch) | Hydroxychloroquine (anti-malarial) | Tolterodine (urology) | Quinine (e.g cramps) |
| Sildenafil |
|
|
|
MILD/LOW EFFECT
The following drugs can also cause a QT prolongation but the effect is usually MILD or LOW. (i.e. less than 10 msec). Usually you don’t need to worry. However, the effect can be greater and therefore more serious if you use a combination of the mildly prolonging QT interval drugs. So be careful with co-prescribing these drugs in the same patient.
Lots of things can cause a prolonged QTc…here are just a few:
General Principles…
Writing a prescription…
The following will save NHS costs…
Place drug onto repeat template if:
And remember…
This is what you need to do when you receive a script request from the patient, the first thing to do is CHECK THE MEDICATION REVIEW DATE
TASKS
How to review medication
Review pathology results as required:
KEY POINTS
Prescriptions can be requested:
When reviewing repeat medications
DEMENTIA
– Degree of cognitive impairment leading to sig. Memory problems, a degree of disorientation, or a change in personality & unable to self care
– MiniCog tool (easy to use assessment tool)
– HbA1c target: 60-70mmol/mol
END OF LIFE CARE
Signing prescriptions:
List of Drugs that need monitoring
ANTIPSYCHOTICS – like Amisulpride, Aripiprazole, Chlorpromazine, Clozapine, Flupentixol, Haloperidol, Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, Sulpiride, Trifluoperazine, Zuclopenthixol
AMBER DRUGS – see list below
Don’t forget Amiodarone
Alcohol withdrawal | |
Mild to moderate dementia in Alzheimer’s disease | |
Dopaminergic drug – Parkinson’s disease | |
Treatment of ADHD | |
Immunosuppression | |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease | |
Immunosuppression in adults | |
Renal | |
Secondary hyperparathyroidism in end stage Renal disease | |
Treatment of colonisation and infections of the lung due to pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
Primary and secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women | |
Treatment of ADHD | |
Phosphorylated glycosylated recombinant hyman deoxyribonuclease 1 (rhDNase) – Cystic Fibrosis | |
Renal Anaemia | |
Breast Cancer | |
Treatment of grass pollen allergies | |
TBC | |
DMARD and immunosupression | |
Metastatic bone disease | |
Treatment of depressive illness | |
Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug | |
Attention Deficity Hyperactivity Disorder | |
Affective disorders and cluster headaches | |
Sleep disorders | |
Immunosuppression | |
Treatment of ADHD | |
For the management of Status Epilepticus in adults and children | |
Narcolepsy | |
Immunosuppression | |
Mycophenolate Mofetil or Mycophenolic Acid (Myfortic) Post Solid Organ Transplant | Post renal transplant |
Alcohol relapse prevention | |
Treatment of narcotic addiction | |
Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug – rheumatoid arthritis | |
Treatment of depressive illness | |
Chemoprevention of amilial breast cancer | |
Treatment of amytrophic lateral sclerosis | |
Immunosuppressant post renal transplant | |
Sodium Aurothiomalate (Gold Injection) in Rheumatoid Arthritis | Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug – rheumatoid arthritis |
Somatostatin Analogues (Somatuline LA, Somatuline Autogel and Sandostatin LAR) * | Somatostatin Analogue – licensed indications (symptoms associated with carcinoid tumours with features of carcinoid syndrome, VIPomas, glucagonomas, acromegaly, prevention of complications following pancreatic surgery) |
DMARD and immunosupression | |
Immunosuppression post transplant | |
Chemoprevention of familial breast cancer | |
Treatment of male hypogonadism menopausal symptoms in women | |
Cystic fibrosis management | |
Treatment of depressive illness | |
Cluster headaches |
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Generally
Don’t forget – follow the WHO pain ladder, starting with Paracetamol if needs be, then co-codamol, co-dydramol, tramadol etc. Don’t just give randomly. If you ever get stuck with a patient’s pain control, go back to the WHO pain ladder.
NSAIDs: remember, Naproxen better than ibuprofen. Better safety profile, stronger. Needs to give PPI if over age 65 OR high risk factors. High risk factors: PMH of gastric/duodenal ulcers, GI bleeding, blood thinning agents, aspirin 300mg, prednisolone, SSRIs (yes, SSRIs can increase risk of GI bleeds). COX2 inhibitors better than ibuprofen and naproxen for GI risks.
NSAID gels: Would gels be safer than oral NSAID? Ibugel. Voltarol gel. Piroxicam gel Ketoprofen gel
COX2 inhibitors or high dose ibuprofen (<2400mg daily): do NOT prescribe if patient has IHD, PVD, CVD, CHF grade 2-3. Also don’t give COX2 inhibitors to those with Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
Other Non-opioids: think amitriptyline, gabapentin (generally try and avoid pentins if you can)
More about the COX-2 inhibitors
NSAIDs reduce the production of prostaglandins by inhibiting the enzyme cyclo-oxygenase. They vary in their selectivity for inhibiting different types of cyclo-oxygenase (COX1 and COX2). Naproxen and Ibuprofen inhibit both COX1 and COX2. COX2 inhibitors like etoricoxib and celecoxib, inhibit only cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) – which is associated with less gastro-intestinal intolerance.
A rundown of the NSAIDs
Steroid Cream Strength
Be careful with prescribing a medicine which may cause dependence . As a doctor, don’t take the easy way out by providing a quick fix to chronic pain or difficulties by simply prescribing these sorts of drugs. Instead, discuss alternative ways of managing the pain or difficulty (coping mechanisms), optimise their lives (e.g. otherways to improve mood and happiness, mindfulness) and empower the patient. And whilst we say avoid their use generally across all age groups, especially avoid in those under age 65. Remember, starting a person even at the age 66 means they’re likely to be on them for 15 years (average life expectancy about 83) – and in that time, they will want more and more, year on year! These drugs in higher doses as more and more get pile on then start destroying the lives of these patients. The number of patients who say how amazing their lives are when they gradually withdraw from years of being hookeed is quite high. The top 4 culprits are
Ferrous fumarate/sulphate or Folic acid – issue 3/4m course. That’s what is needed to get the stores back up. Don’t repeat bloods until 3m is up.
Propranolol – remember, if your patient has a moderate to high suicidal risk, do not prescribe – high risk of death in suicidal attempts! Propranolol is used to treat several medical conditions, including migraine, cardiovascular problems, and the physical effects of anxiety. But there has been a rise in propranolol overdose deaths in the last few years (2020). If prescribing, tell patients about the possible severe consequences of overdose with propranolol and that it can cause death. Prescribers should be mindful of quantities supplied on a prescription, particularly where there is a significant risk of overdose. Where an opportunity arises, please consider reviewing the ongoing need for propranolol.
HOW MUCH SHOULD BABIES BE FEEDING?
Prescribing is an integral part of a General Practitioner’s work and several high profile cases have been published when qualified doctors have made catastrophic errors. Because there are a large number of patient deaths relating to medication errors. The only way this will improve is if we start regularly reviewing and analysing our prescribing habits. The best way of looking at an identified need is to pause and reflect on what we are doing rather than bury our heads and just continuing as we are. Would you agree?
We know GP trainees appear to assessed left-right-and centre. But this is another important area where we can better ourselves. Qualified GPs and their practices are often asked to look at their prescribing habits in some way or another and we feel therefore trainees should too.
All prescribing GPs are expected to demonstrate the following, across people of all ages which includes extremes of age, for example babies, children and older people with frailty (based on the GMC GPCs 2017). The items on the right are the proficiencies being assessed.
All trainees in ST3 have to do one. There is no set standard as it is designed as a learning exercise; however if no errors are highlighted and if no learning is identified this would raise concerns, as to date this has never been the case.
For the official MRCGP prescribing tools and supporting documents to help you, see the resource items under the QUICKLINKS section at the top of the page. They are reproduced below for your convenience.
You are required to collect the data for 50 prescriptions. Many of you will be able to use the created searches below to help facilitate the gathering of the data.
Some of you will unfortunately not be able to use this functionality, either because of the system you are using or because of how you are set up as a user on the system. If that is the case then you will need to complete this assessment by looking through all of your consultations backwards, from a particular date and identifying when you have prescribed a medication. You will then need to manually enter the information onto the spreadsheet.

This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Bradford VTS was created by Dr. Ramesh Mehay, a Programme Director for Bradford GP Training Scheme back in 2001. Over the years, it has seen many permutations. At the time, there were very few resources for GP trainees and their trainers so Bradford decided to create one FOR EVERYONE.
So, we see Bradford VTS as the INDEPENDENT vocational training scheme website providing a wealth of free medical resources for GP trainees, their trainers and TPDs everywhere and anywhere. We also welcome other health professionals – as we know the site is used by both those qualified and in training – such as Associate Physicians, ANPs, Medical & Nursing Students.
Our fundamental belief is to openly and freely share knowledge to help learn and develop with each other. Feel free to use the information – as long as it is not for a commercial purpose.
We have a wealth of downloadable resources and we also welcome copyright-free educational material from all our users to help build our rich resource (send to bradfordvts@gmail.com).
Our sections on (medical) COMMUNICATION SKILLS and (medical) TEACHING & LEARNING are perhaps the best and most comprehensive on the world wide web (see white-on-black menu header section on the homepage).